16 Finance And Accounting KPIs To Prioritize
Blog post
Share
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are critical to measuring the success of an organization’s overall business strategy. Determining the proper KPIs to track can be tricky, especially when the metrics span the entire financial close process. Automation can simplify this process, making it easier for the Office of Finance to correctly identify KPIs that align with the organization to improve their processes and help determine overall business health and strategy.
In this blog, we will cover important KPIs for finance and accounting that fall into five key categories:
- Holistic Close
- Close Monitoring
- Balance Sheet Reconciliation
- Journal Entry
- Compliance
Holistic Close
Tracking and measuring metrics ensures that the entire financial close process is managed effectively. These give much-needed visibility into the process and the impact of its quality on the organization’s revenue.
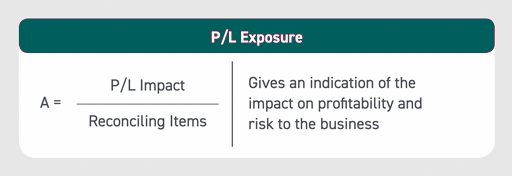
KPI #1: Profit and Loss
The profit and loss metric allows organizations to measure the risk and consequential impact certain items will have on the business. Without this metric, finance and accounting (F&A) teams miss out on a significant analysis that could create an opportunity for future improvement.
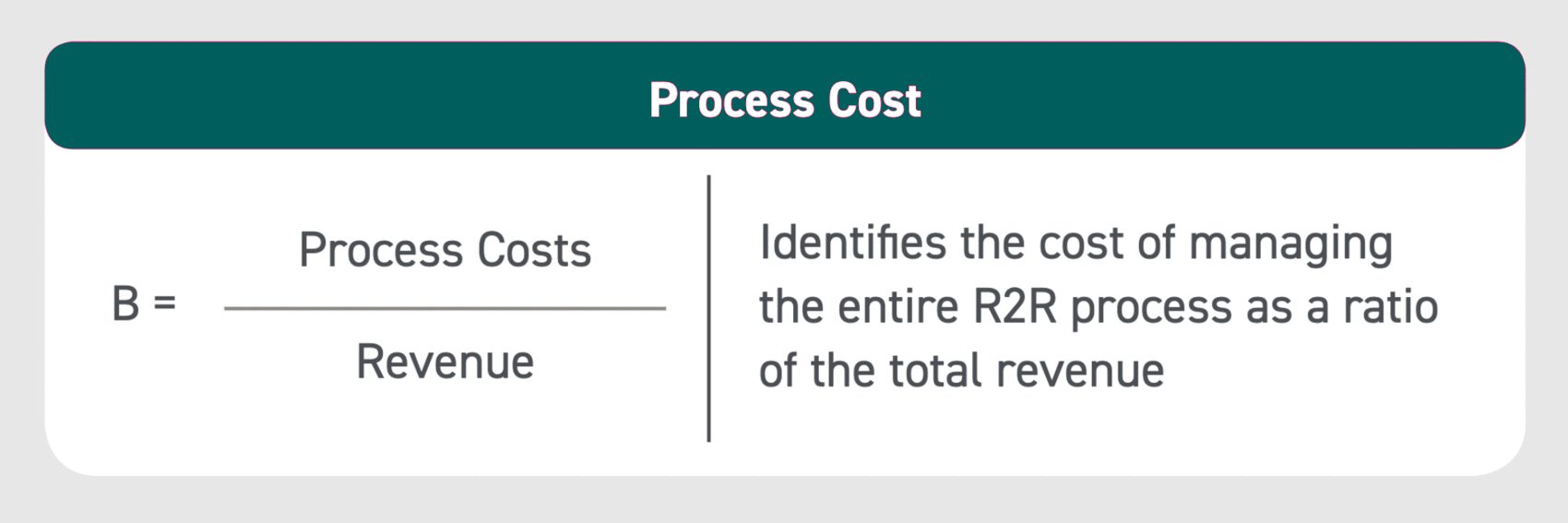
KPI #2: Process Cost
This accounting metric identifies the cost of managing the entire financial close process as a ratio of the total organizational revenue. Leveraging automation technology not only empowers organizations to reduce overall resources and costs but, also enables Offices of Finance to effectively scale their operations to accommodate high-volume transactions.
KPI #3: Time to Close
Time to close is one of the most critical KPIs for F&A teams to track by comparing the number of days it takes to close at the target period. If the actual days to close is higher than the target period, what’s causing the delay? Analyzing this KPI helps gain visibility into a part of the process that otherwise is not transparent.

KPI #4: Close Quality
The close quality KPI utilizes the data from the preview metrics – time to close, process cost, and profit & loss. Analyzing this metric indicates the quality of the overall Record to Report process.

Close Monitoring KPIs
Analyzing close monitoring metrics empowers Offices of Finance and leaders to have more confidence in the consolidated management report that is filed each period.
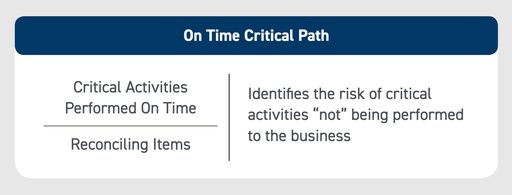
KPI #5: On-Time Critical Path
What is the impact of critical financial close activities not performed — whether that means never performed or not performed by the deadline? Too many necessary activities left incomplete or not completed on time can significantly raise an organization’s risk profile. By analyzing on time critical path, F&A teams gain deeper insight into activities that have met deadlines, were incomplete or late.
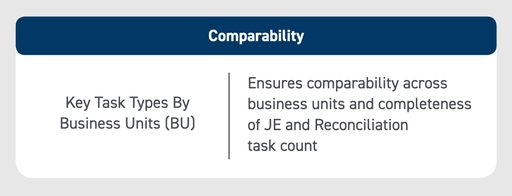
KPI #6: Comparability
This financial close metric is focused on comparing the number of task types per business unit (BU) to evaluate the distribution and completeness of financial close tasks. Instead of placing the burden of close tasks on a select few people, delegating tasks enables accountants to have a more evenly distributed workload — further reducing the amount of overtime and instances of burnout.
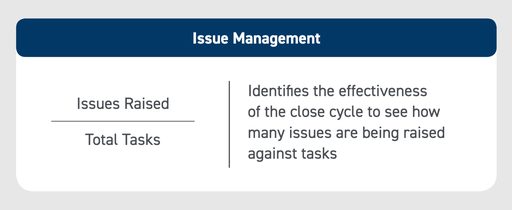
KPI #7: Issue Management
Issue management identifies the ratio of issues raised in the close process to the total tasks performed. A high percentage of issues raised should alert finance leadership to inefficiencies that could lead to lower quality tasks.
Reconciliation KPIs
The balance sheet reconciliation process is the foundation of the entire financial close process. To that end, it should be measured and optimized correctly. There are three crucial KPI examples for finance departments to analyze in the reconciliation process, mentioned below.
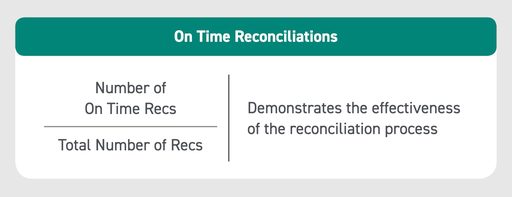
KPI #8: On-Time Reconciliations
The on-time reconciliations KPI helps analyze the efficiency of the balance sheet reconciliation process. A lower number of on-time reconciliations might indicate process bottlenecks that need to be solved.
KPI #9: Number of Aging of Reconciling Items
This metric gives leadership insight into how long specific tasks have been assigned and indicates which tasks should be prioritized.

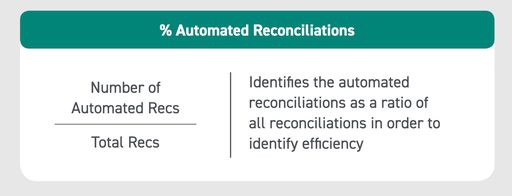
KPI #10: Percentage of Automated Reconciliations
This metric becomes essential when balance sheet automation is brought into the process. One of the benefits of automation in accounting is a reduced workload for finance staff because automation can handle certain low-risk reconciliations.
Journal Entry KPIs
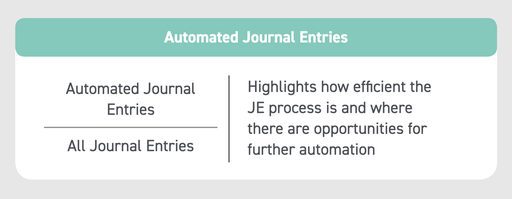
KPI #11: Automated Journal Entries
As mentioned before, what can be handled by automation should be, and the journal entry process is a great example. If your organization has implemented automation, analyzing this metric can help dig into the ROI that automation is bringing to the organization and can identify if automation can do more in the journal entry process.
KPI #12: Timely Journal Approval
One of the major bottlenecks in the journal entry process is the approval process. This metric helps gain visibility into how efficient the journal entry process is by measuring how many days it took for journals to be posted.

KPI #13: Journal Entry Quality
Efficiency is nothing without effectiveness, but truly measuring effectiveness is complicated. The journal entry quality KPI helps measure effectiveness by comparing the number of rejected journals to the number of total journals raised.

Compliance KPIs
Last, but certainly not least, are the accounting KPIs specific to compliance. These metrics will evaluate the effectiveness of corporate and regulatory compliance controls across the organization. If an organization’s internal controls are not properly addressed, then these metrics will highlight the need for an effective compliance framework that remediates issues before financial reporting is completed.
KPI #14: Cost of Compliance
The cost of compliance KPI measures the total cost of the organizations’ compliance framework.

KPI #15: Issue Time to Resolution
This metric identifies the period from when an issue is caught to the time the issue is solved. This is an increasingly important metric that auditors want to know, and internal stakeholders will also want to measure.

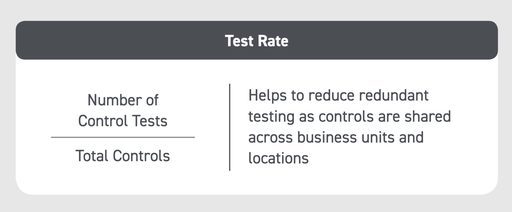
KPI #16: Test Rate
Upkeep of the control environment is as vital as implementing an effective control environment. The test rate KPI enables finance leadership by identifying if controls are being adequately tested to ensure functionality.
Prioritize KPIs in Finance and Accounting
The KPI examples for F&A teams outlined here represent the best practices and starting points for achieving goals such as reducing days to close or improving the quality of the journal entry process. Leading organizations prioritize and measure these KPIs to drive efficiency and effectiveness within finance and accounting to better support the broader organization.
Written by: Lauren McCrohan