What Is An Accounting Journal Entry?
Blog post
Share
An accounting journal entry is more than just numbers – these numbers tell exactly which accounts were affected, by how much, and when. Journal entries are often referred to as the most important skills for accountants to learn because they determine the company’s financial statements. Based on how accurate those journal entries are, plans can be built out for possible business expansions and new hires and can answer questions about the company’s finances.
Understanding An Accounting Journal Entry
As the name suggests, journal entries were recorded in journals long before software and in that journal would be a record of all transactions in chronological order. To this day, every journal entry recorded is to be equal in debits and credits to keep the classic equation of Assets = Liabilities + Shareholders’ Equity in balance. For each journal entry, consider these elements:
- Which accounts are affected by the transaction?
- Does the affected account increase or decrease?
- How much is changed in each account?
- Are the overall debits and credits in balance?
What are Debits and Credits?
An accounting journal entry follows the previously mentioned equation:
Assets = Liabilities + Shareholders’ Equity
Debits will fall to the left side of the equation and Credits on the right. Debits add to expense and asset accounts and subtract from liability, revenue, and equity balances. On the other hand, Credits subtract from expense and asset balances, while adding to liability, revenue, and equity accounts. This concept of a transaction affecting two accounts, where one is debited, and the other is equally credited is known as double-entry bookkeeping.
The 6 Types of Journal Entry Format
All six types of journal entries have their unique purpose in accounting. Combined all together, these journal entries produce an accurate understanding of the company’s finances.
- Opening Entries: These entries carry over the closing balance from the previous accounting period as the opening balance for the current account period. So, in the case that $5,000 was the ending balance of the Cash account from the previous accounting period – the $5,000 balance will now be the opening entry for the current accounting period.
- Transfer Entries: These entries move or allocate an expense or income from one account to another. If JK Inc. wanted to transfer cash from its main account to a subsidiary, a transfer journal entry is required to make this happen.
- Closing Entries: These entries mark the end of an accounting period at a particular balance which is later transferred from a temporary to a permanent account. Temporary accounts can be the following: expense and loss accounts, revenue, income and gain accounts, income summary accounts, and dividend or withdrawal accounts.
- Adjusting Entries: Entries that record changes to accounts that do not otherwise account for in the journal, in compliance with the accrual method of accounting. Adjusting entries are entered at the end of the accounting period into the general ledger per matching and revenue recognition principles.
- Compound Entries: These entries affect more than two accounts where certain accounts may be credited or debited more than once. Thus, compound entries do not follow the traditional rule of a journal entry and often have an unequal number of debits and credits.
- Reversing Entries: Used to clarify bookkeeping, reversing entries are made at the start of a new accounting period to reverse adjusting entries made in the previous period.
Journal Entry Format and Elements
Below is the general format used to create an accounting journal entry:
- At the very top is the Header – descriptor of the entry type and the date of entry to the journal.
- A unique identifier – usually known as the Reference Number.
- The account(s) and the amount(s) to be debited by the transaction and the date(s) these debits are made.
- The account(s) and the amount(s) to be credited by the transaction and the date(s) these credits are made.
- Description of the transaction.
To serve as an example:
(Capital-related examples)
Uncle T started his business, Uncle T’s Auto Insurance, on June 20th, 2022 with $20,000.00 cash and $6,000.00 worth of furniture.
| Date | Reference Number | Description | Debit | Credit |
| June 20th, 2022 | 0001 | Cash | $20,000.00 | |
| June 20th, 2022 | 0001 | Office Furniture | $6,000.00 | |
| June 20th, 2022 | 0001 | Capital | $26,000.00 |
On July 1st, 2022, Uncle T deposited $25,000.00 into a newly opened business bank account.
| Date | Reference Number | Description | Debit | Credit |
| July 1st, 2022 | 0002 | Cash | $25,000.00 | |
| July 1st, 2022 | 0002 | Capital | $25,000.00 |
On July 15th, 2022, the salaries of four employees amounted to $12,000.00. Also, office resources from June were purchased on credit.
| Date | Reference Number | Description | Debit | Credit |
| July 15th, 2022 | 0003 | Salaries Expense | $12,000.00 | |
| July 15th, 2022 | 0003 | Cash | $12,000.00 | |
| July 15th, 2022 | 0003 | Office Resources | $400.00 | |
| July 15th, 2022 | 0003 | Accounts Payable | $400.00 |
On July 31st, 2022, monthly expenses rolled in with office rent at $1,500.00, $300.00 for utilities, and $400.00 for office resources.
| Date | Reference Number | Description | Debit | Credit |
| July 31st, 2022 | 0004 | Rent Expense | $1,500.00 | |
| July 31st, 2022 | 0004 | Cash | $1,500.00 | |
| July 31st, 2022 | 0004 | Utility Expense | $300.00 | |
| July 31st, 2022 | 0004 | Cash | $300.00 | |
| July 31st, 2022 | 0004 | Accounts Payable | $400.00 | |
| July 31st, 2022 | 0004 | Cash | $400.00 |
(Revenue-related examples)
On June 29th, 2022, Uncle T’s Auto Insurance sold 12 different semi-annual auto-insurance plans amounting to $15,450.00.
| Date | Reference Number | Description | Debit | Credit |
| June 29th, 2022 | 0005 | Accounts Receivable | $15,450.00 | |
| June 29th, 2022 | 0005 | Deferred Revenue | $15,450.00 |
On July 18th, 2022, Uncle T’s Auto Insurance received payment for a customer invoice for semi-annual policies.
| Date | Reference Number | Description | Debit | Credit |
| July 18th,2022 | 0006 | Cash | $1,200.00 | |
| July 18th,2022 | 0006 | Account Receivables | $1,200.00 |
July 31st, 2022, the business recognized one-month revenue on the twelve different semi-annual policies from June 29th.
| Date | Reference Number | Description | Debit | Credit |
| July 31st, 2022 | 0004 | Deferred Revenue | $2,575.00 | |
| July 31st, 2022 | 0004 | Revenue | $2,575.00 |
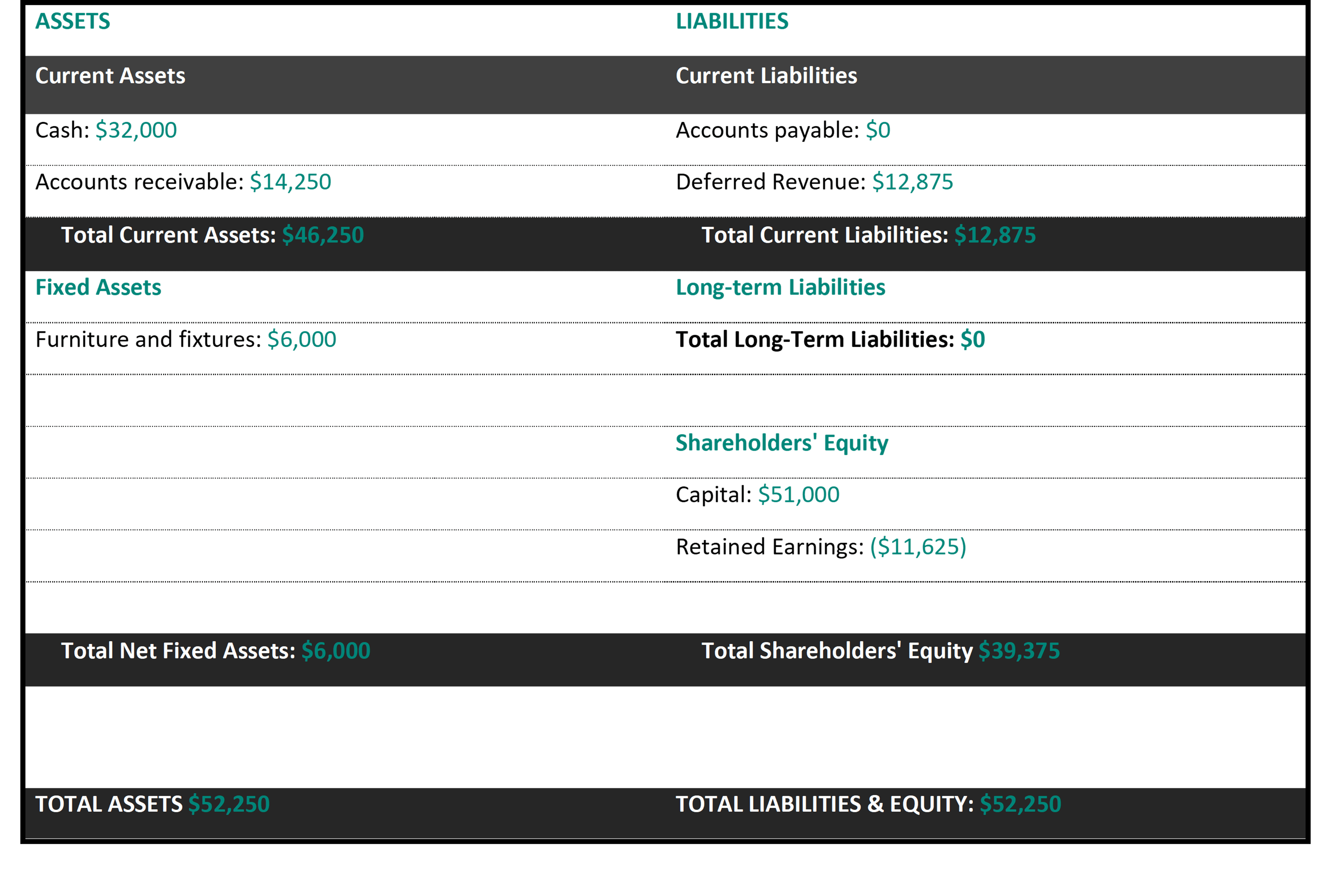
As of July 31st, 2022, here is a look into the current financial position and performance of Uncle T’s Auto Insurance after the first two months of operations.
Balance Sheet as of July 31, 2022
Income Statement for the period ended July 31, 2022
| Revenue | 2022 |
| Sales Revenue | $2,575 |
| (Less Sales Returns and Allowances) | $0.00 |
| Service Revenue | $0.00 |
| Interest Revenue | $0.00 |
| Other Revenue | |
| Total Revenues | $ 2,575 |
| Expenses | |
| Rent Expense | $1,500 |
| Utilities | $300 |
| Office Supplies | $400 |
| Salaries Expense | $12,000 |
| Total Expenses | $ 14,200 |
| Net Income Before Taxes | $ (11,625) |
| Income Tax Expense | $0.00 |
| Net Income | ($11,625) |
The Accounting Journal Entry process does not have to be difficult or time-consuming
Journal entries aren’t always difficult, but manually inputting every single line item can result in human errors when there are hundreds, or even thousands of journals to create every financial period. Relying on journal entry automation to bring in data from bank feeds and import functions, your accounting team can see a quicker accounting process while having greater accuracy.
Save your team the time and give them peace of mind with Trintech’s Cadency solution. In addition to a more efficient and accurate journal entry process, teams can prioritize and focus more on tasks that cannot be automated while also bringing a more simplified close process.
Written By: Jae Kim
Learn more in our Finance & Accounting Glossary
Find this content helpful?
If you loved this blog, there’s more where that came from! Discover additional ways that Trintech can help you streamline your financial processes:






